Thyroid hormone regulating drugs
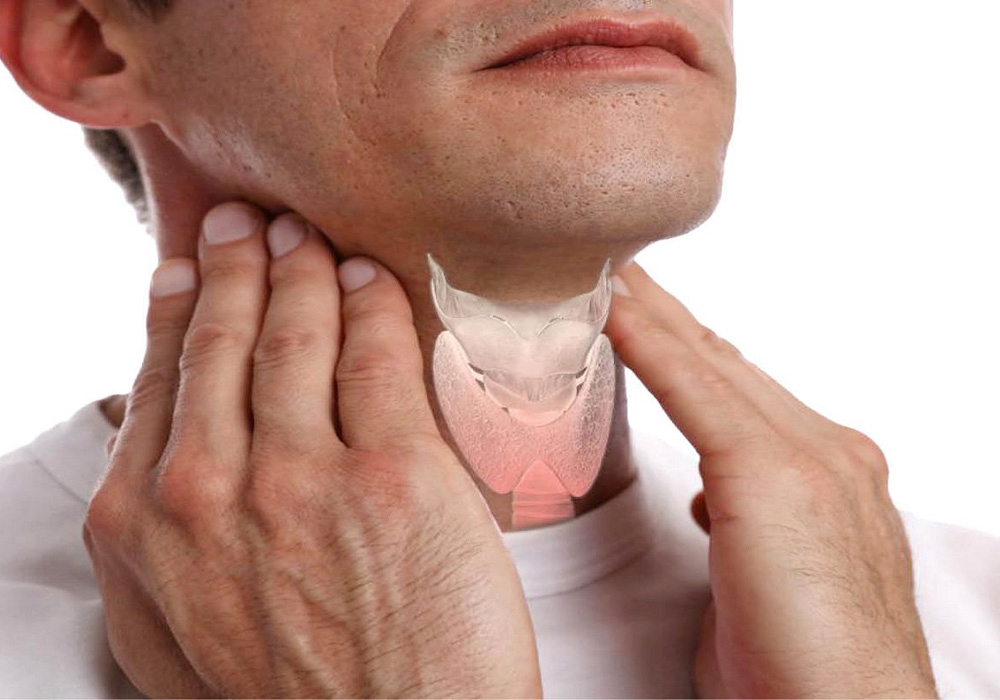
The thyroid gland is responsible for secreting the thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) hormones.
What is thyroid?
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland, located in the front of the neck. The thyroid gland is responsible for secreting the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are released into the bloodstream and increase the rate of energy production in the body. In healthy people, this gland secretes enough hormones. These hormones regulate metabolism
Hyperthyroidism causes large amounts of hormones to reach the body organs. Patients feel warmer due to increased metabolism. Despite more consumption of food, they also lose weight.
Hypothyroidism causes the secretion of hormones to be less than standard. The disease causes symptoms such as weight gain despite anorexia and extreme fatigue. Hair loss, shortness of breath and constipation are other symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Introducing the most common thyroid disease controlling drugs
Drugs used to treat thyroid disease fall into two main categories. These categories are related to hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. Common medications for hyperthyroidism include
- Carbimazole
- Propylthiouracil
- Methimazole
Common medications for hypothyroidism include:
- Levothyroxine sodium
- Sodium Liothyronine